Docs
Concepts
Concepts
At the core of llm-ui is useLLMOutput. This hook takes a single chat response from an LLM and breaks it into blocks.
Blocks
useLLMOutput takes blocks and fallbackBlock as arguments.
blocksis an array of block configurations thatuseLLMOutputattempts to match against the LLM output.fallbackBlockis used for sections of the chat response when no other block matches.
We could pass:
blocks: [codeBlock]which matches codeblock starting with```.fallbackBlock: markdownBlockwhich assumes anything else is markdown .
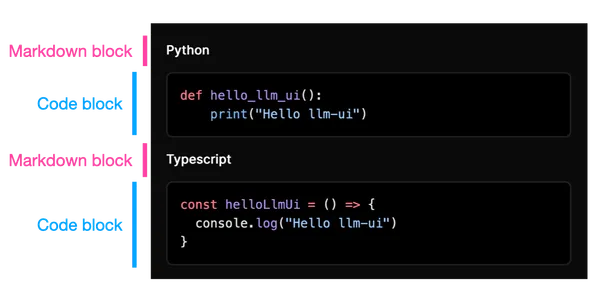
useLLMOutput will then break the chat response into code and markdown blocks:
## Python
```python
def hello_llm_ui():
print("Hello llm-ui!")
```
## Typescript
```typescript
const helloLlmUi = () => {
console.log("Hello llm-ui!");
};
```
llm-ui breaks this example into blocks:
Throtting
useLLMOutput also takes throttle as an argument. This function allows useLLMOutput to lag behind the actual LLM output.
Here is an example of llm-ui’s throttling in action:
# H1
Hi Docs
```typescript
console.log('hello')
```0.4x
The disadvantage of throttling is that the llm output is delayed in reaching the user.
The benefits of throttling:
- llm-ui can smooth out pauses in the LLM’s streamed output.
- Blocks can hide ‘non-user’ characters from user (e.g.
##in a markdown header).